Phase Change Cold Plate Liquid Cooling
•Phase change cold plate liquid cooling primarily consists of a primary side and a secondary side. The primary side is the outdoor side, while the secondary side is the indoor side. Heat exchange between the two sides is facilitated by a CDU (Cooling Distribution Unit).
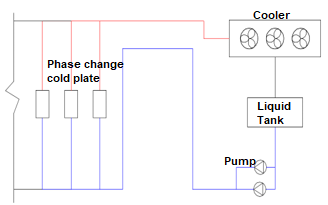
•The secondary side's chip phase-change cold plate consists of efficient microchannel two-phase cold plates, molded pipelines, and self-sealing joints. It is mainly used for targeted heat dissipation of high-power chips such as server CPUs and GPUs.
•On the primary side, the heat dissipation can be achieved by dispersed heat sinks, as well as dry coolers and cooling towers for centralized heat dissipation.
•The phase-change cold plate mainly removes 60% to 80% of the heat (including that from CPUs/GPUs), while the remaining heat is dissipated by back panel air conditioning, wind walls, or traditional air conditioning systems.
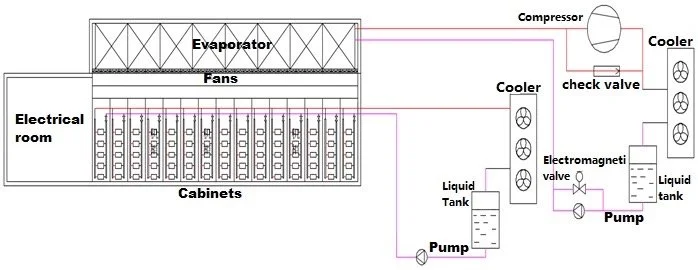
•Containerized setup includes cabinet bases, raised flooring, and a secondary side pipe network design, positioned beneath the floor, with overhead electrical wiring for enhanced safety.
•Two CDUs are arranged in a 1+1 backup configuration, with intermediate column head cabinets and cabinets.
•Containers need effective anti-condensation measures, such as insulation on the bottom and around the perimeter. External cooling/heating air conditioning units or wind walls can be installed, with vents facing inside the container to prevent high temperatures in summer and deviations from TIA942 standards in temperature and humidity during extreme winter weather.